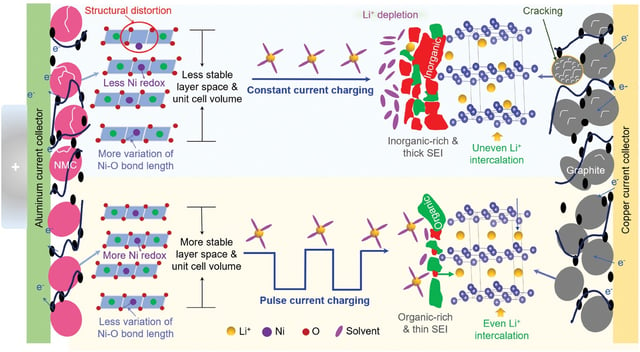
Overview
- The new 'pulse current' charging technique alternates high-frequency bursts of energy, reducing mechanical stress on battery electrodes.
- Studies show that this method can potentially double the cycle life of batteries, with up to 80% capacity retention.
- Pulsed current charging leads to thinner solid electrolyte interfaces and less structural damage compared to constant current charging.
- Advanced spectroscopy techniques have revealed that this method promotes a more uniform distribution of lithium ions.
- The technology has significant implications for electric vehicles and portable electronics, promising longer-lasting batteries.