Overview
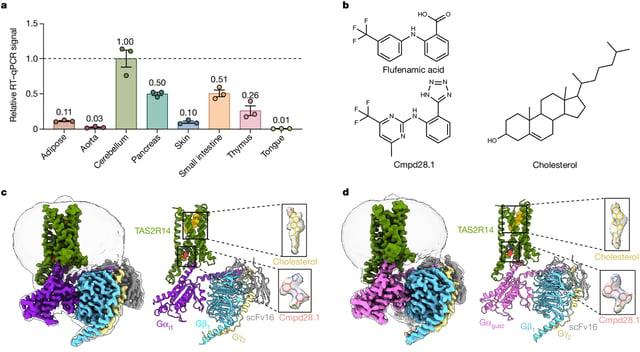
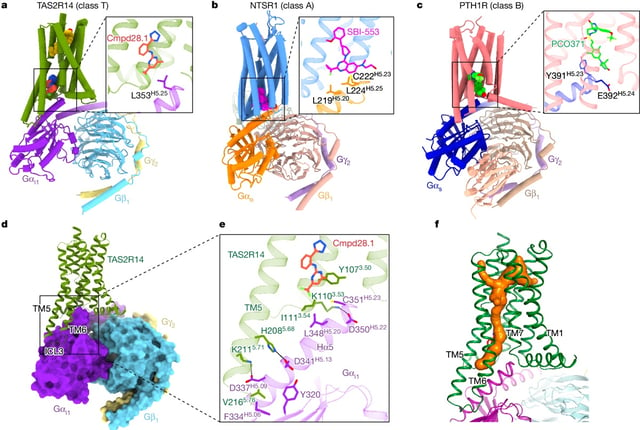
- A breakthrough study using cryo-electron microscopy has mapped the structure of the human bitter taste receptor TAS2R14.
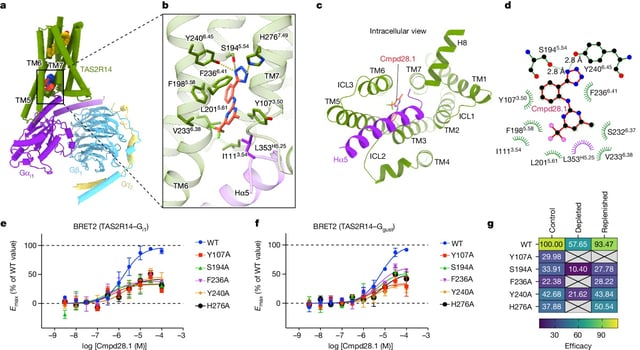
- Cholesterol and specific intracellular compounds bind at two distinct sites on TAS2R14, leading to its activation.
- This dual binding mechanism suggests a complex activation process that could influence future drug design.
- The findings may have implications for treating metabolic diseases by targeting taste receptors.
- Further research is planned to explore the role of TAS2R14 in other organs, which could have broader physiological implications.