Overview
- Researchers from Chalmers University and Harvard University analyzed over 200,000 UK Biobank participants to validate the predictive power of apoB and lipoprotein(a) markers.
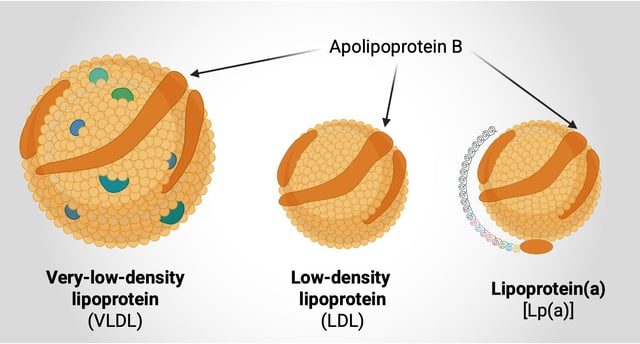
- The study found that apoB particle count is the most accurate single measure for assessing heart disease risk, outperforming traditional cholesterol tests.
- Lipoprotein(a), a genetically determined marker, was identified as a critical complement to apoB for a comprehensive risk profile.
- Standard cholesterol tests may underestimate risk in one in 12 patients, potentially missing high-risk individuals who could benefit from early intervention.
- Both apoB and lipoprotein(a) tests are commercially available, low-cost, and positioned for integration into routine clinical practice to improve cardiovascular outcomes.