Overview
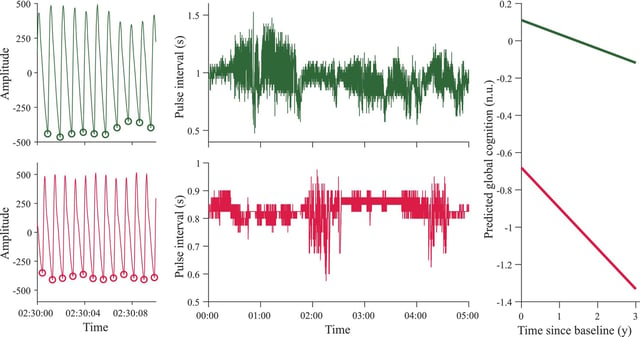
- A study published in May 2025 demonstrates that pulse rate complexity, measured via wearable pulse oximetry, predicts cognitive decline more effectively than traditional heart rate variability metrics.
- Researchers analyzed data from 503 older adults, averaging 82 years old, monitored over 4.5 years as part of the Rush Memory and Aging Project.
- The Itamar WatchPAT 300 device captured overnight pulse rate data, enabling the application of nonlinear dynamical analysis to assess heart rhythm complexity.
- Higher pulse rate complexity at baseline correlated with slower cognitive decline, suggesting a link between cardiovascular adaptability and neural health.
- Future research will explore whether this measure can predict dementia onset, potentially guiding early interventions for at-risk individuals.