Overview
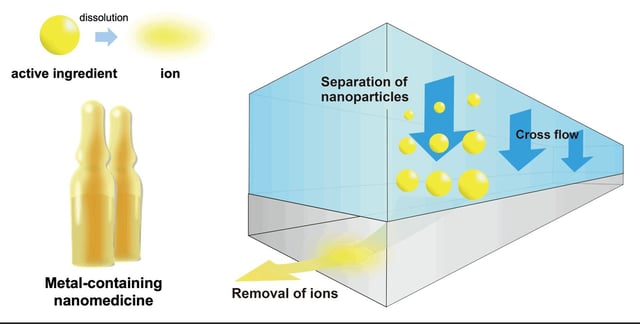
- Researchers from Chiba University pioneered a workflow that integrates asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for detailed compositional analysis of metal-based nanomedicines.
- Testing on Resovist® showed that free ionic iron constituted only 0.022% of total iron content, underscoring the contrast agent’s stability and low toxicity risk.
- The method exploits AF4’s initial focus step to filter out dissolved ions before size-based separation of nanoparticles and subsequent ICP-MS quantification of elemental content across particle fractions.
- By distinguishing chemical species of elemental impurities, the assay addresses limitations in current International Council for Harmonization guidelines and enables more precise safety and quality assessments.
- Demonstrated versatility with silicon and iron samples, the technique offers applications beyond pharmaceuticals, including cosmetics and environmental metal monitoring.