Overview
- Two peer-reviewed papers published Sept. 24–25 detail how specific DNA junctions actively maintain meiotic structure and control break formation.
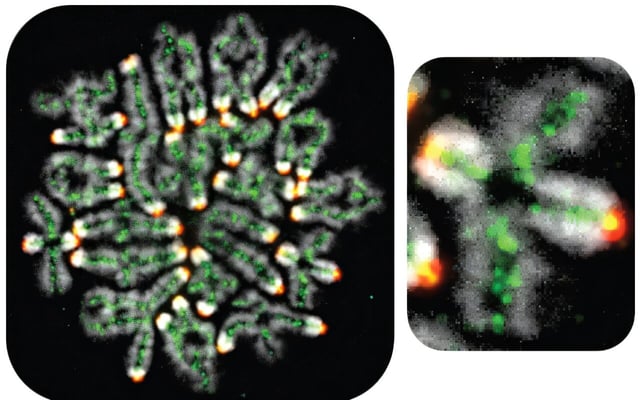
- Hunter’s team shows that a protein network, including cohesin, protects double Holliday junctions from premature dismantling by the STR/Bloom complex to ensure crossovers form.
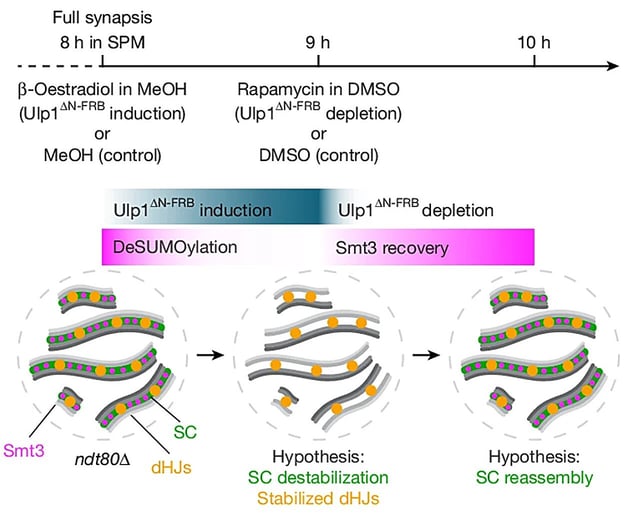
- Matos’s group demonstrates that cutting these junctions in synchronized yeast causes the synaptonemal complex to collapse immediately and restarts DNA breaks, stalling meiosis.
- The work relied on synchronized budding yeast, conditional protein degradation, and a targeted junction-cutting tool to track cause and effect in real time.
- Researchers say the next step is to test whether this protection and feedback operate in mammals, with potential implications for understanding human fertility and genome stability.