Overview
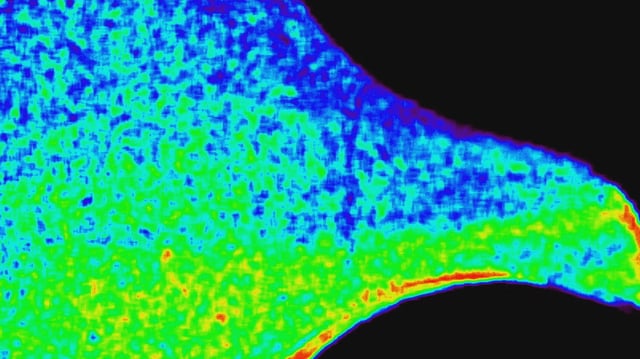
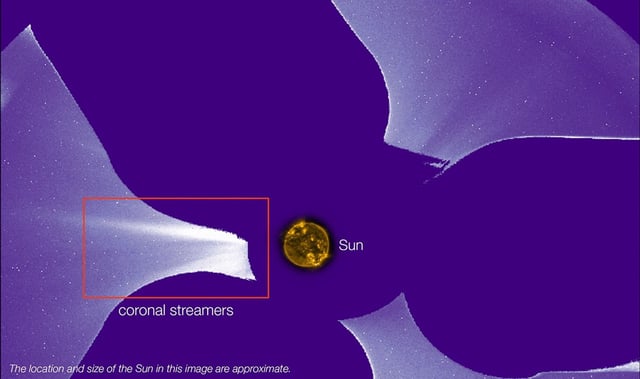
- The coronagraph-style CODEX instrument uses occulting disks and four narrow-band filters to isolate the solar corona and measure its temperature and wind speed.
- Initial analysis of CODEX images revealed non-uniform plasma flows, with localized hot and cool regions indicating sputtering gusts in the corona.
- Data presented at the American Astronomical Society meeting in Anchorage demonstrates CODEX’s successful mapping of solar wind dynamics.
- Measurements of heat alongside flow rates in the corona will provide critical constraints for next-generation space weather models.
- The project brings together NASA Goddard, the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute and Italy’s National Institute for Astrophysics.