Overview
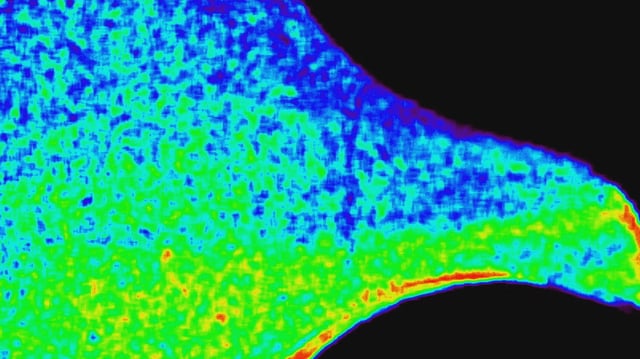
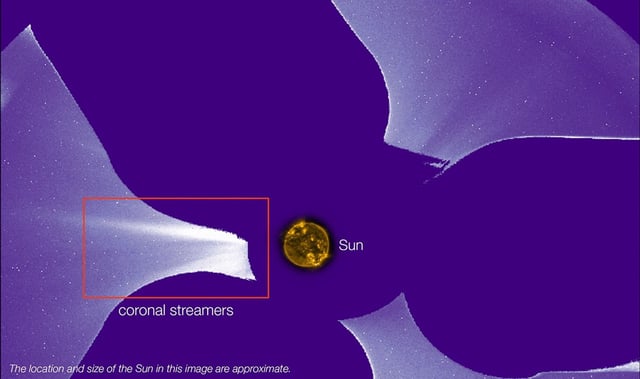
- CODEX’s coronagraph installed on the International Space Station employs occulting disks to simulate solar eclipses and reveal the Sun’s faint corona.
- Four narrow-band filters enable the instrument to extract simultaneous temperature-sensing, speed-tracking data of solar wind plasma.
- Recent analysis shows the corona is characterized by sputtering gusts of hot plasma rather than a uniform outflow.
- Continuous data streams from CODEX are being integrated into space weather models to improve predictions of solar wind impacts on Earth.
- The experiment brings together NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, KASI and INAF in an international collaboration advancing solar physics.