Overview
- The Gannon storm, named after physicist Jennifer Gannon, unexpectedly turned a NASA simulation into a real-world test on May 10, 2024, marking the most severe geomagnetic storm in 20 years.
- The storm caused record thermospheric heating of 1,150°C, leading to atmospheric expansion that increased satellite drag, prematurely deorbiting NASA’s CIRBE CubeSat and disrupting other missions.
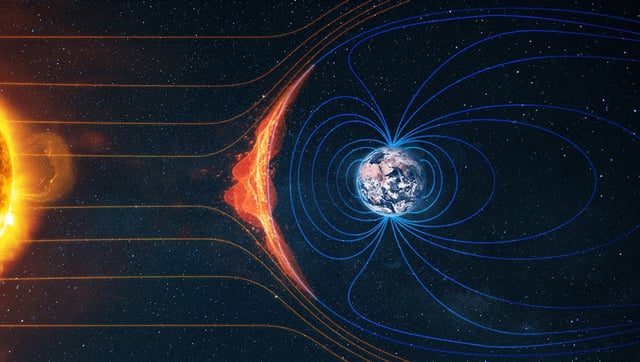
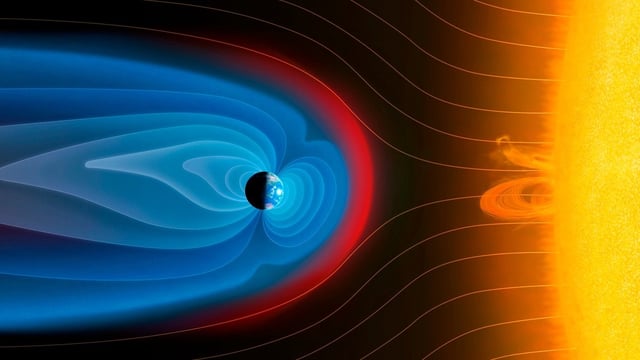
- NASA's MMS and THEMIS-ARTEMIS missions observed the largest magnetospheric electrical currents in two decades, while the CIRBE experiment identified two temporary radiation belts between the Van Allen belts.
- Global infrastructure was impacted, with GPS-guided farming errors costing Midwest farms $17,000 each on average, trans-Atlantic flight reroutes, and power grid disruptions from transformer overheating.
- Unusual magenta auroras observed in Japan revealed new atmospheric processes, while NASA continues to refine predictive models to mitigate risks as solar activity peaks in 2025.