Overview
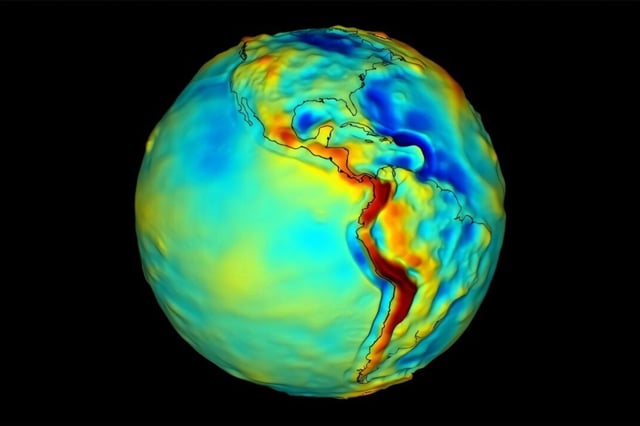
- NASA, in collaboration with private companies and academic institutions, is finalizing the Quantum Gravity Gradiometer Pathfinder (QGGPf) for space-based gravity measurements.
- The QGGPf uses ultra-cold rubidium atoms as test masses to detect subtle variations in Earth's gravitational field with unprecedented sensitivity.
- Compact and lightweight, the instrument is designed to be significantly smaller than traditional gravity sensors, enhancing its suitability for space missions.
- The mission focuses on validating novel quantum technologies, including interactions between light and matter at the atomic scale, ahead of a planned launch later this decade.
- Potential applications include improved Earth mapping, resource management, and insights into planetary science and fundamental physics.