Overview
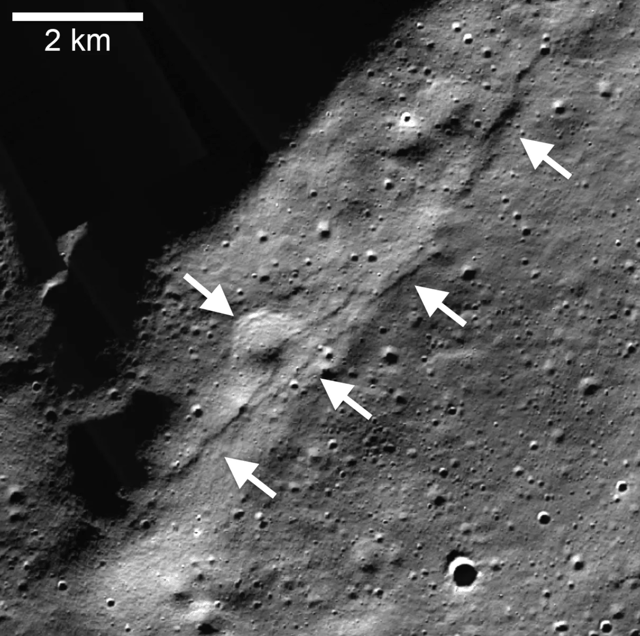
- The moon's core has been gradually cooling over the past few hundred million years, causing the moon's circumference to shrink by more than 150 feet.
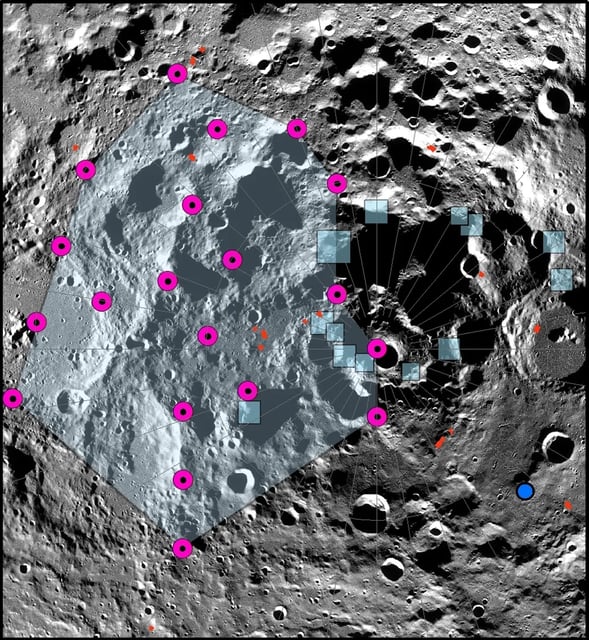
- This shrinkage has led to the creation of faults and the occurrence of moonquakes, particularly in the lunar south pole region.
- Moonquakes can last for several hours and have the potential to cause significant damage to human-made structures on the moon.
- Scientists warn that these seismic activities should be considered when planning future human settlements or missions on the moon, including NASA's Artemis III mission.
- Despite the shrinkage, scientists assure that the moon's mass remains unchanged, and the shrinkage will not affect tidal cycles, eclipses, or full moons on Earth.