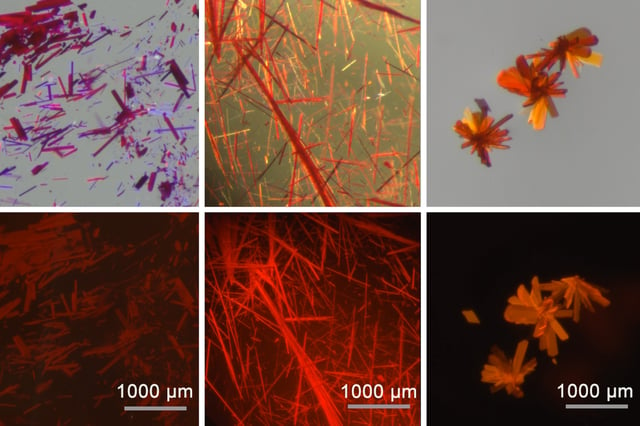
Overview
- Published in Nature Chemistry, the work stabilizes reactive borenium ions using carbodicarbene ligands and engineered counter‑ions.
- Exciton coupling between the borenium cation and selected anions shifts absorption and emission toward the infrared while boosting efficiency.
- The team produced materials as crystals, films, powders, and colloidal suspensions that operate in the red/near‑IR range and resist environmental degradation.
- Researchers plan near‑term cell‑level imaging studies with collaborators at MIT and the Broad Institute, with biomedical use remaining at the laboratory stage.
- They are pursuing deeper near‑infrared emission by incorporating additional boron atoms and designing new carbodicarbenes to preserve stability, with support from the Beckman Foundation and NIH.