Overview
- The study identifies GABA produced by spinal astrocytes via MAOB as a molecular brake that blocks neural regeneration after injury.
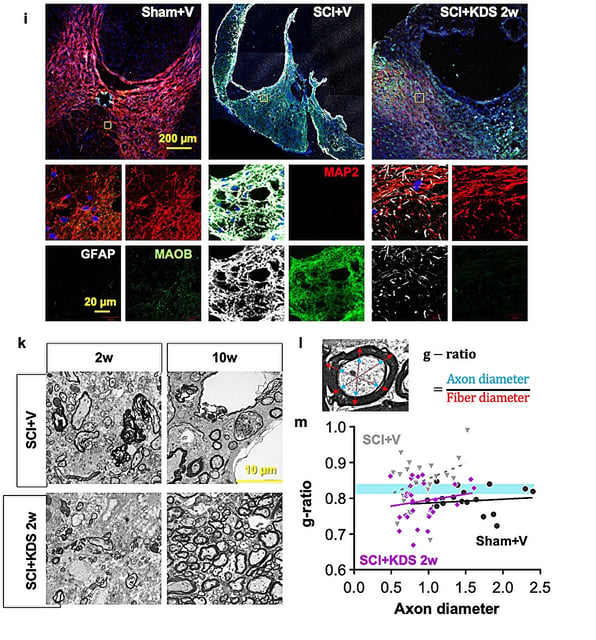
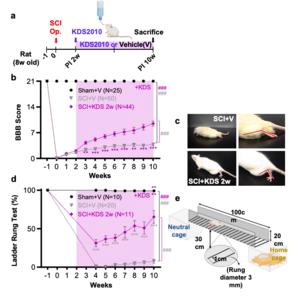
- In rodent models, suppressing MAOB genetically or with KDS2010 restored neuronal MAP2, promoted axonal regrowth and remyelination, and improved locomotion in ladder-walking and gait analyses.
- Increasing MAOB expression in astrocytes caused severe tissue loss with little functional recovery, establishing causal inhibition of repair.
- KDS2010 treatment normalized excessive tonic GABA currents and boosted proBDNF levels, shifting the injury environment toward growth signaling.
- Comparable tissue-preserving benefits were reported in non-human primates, the drug has Phase I safety data in healthy adults, and investigators plan Phase II trials in spinal cord injury patients.