Overview
- Researchers analyzed nearly 90,000 adults from Brazil’s 2019 National Health Survey, finding about one in five reported chronic back pain.
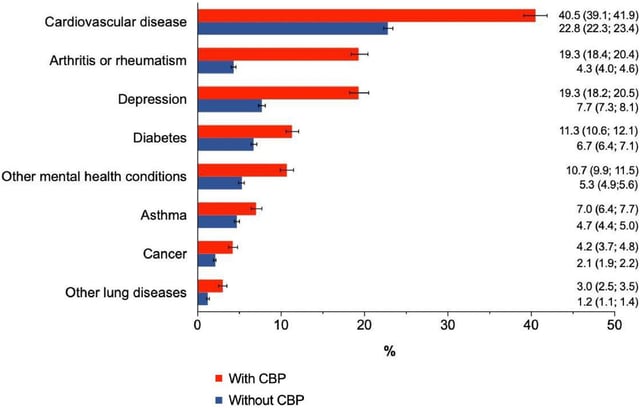
- People with chronic back pain were 17% more likely to report cardiovascular disease, 15% more likely to report arthritis, and 12% more likely to report clinical depression than those without back pain.
- Diabetes, cancer, asthma and other lung diseases were also more prevalent among respondents with chronic back pain.
- Multimorbidity correlated with greater disability, with adults who had both back pain and arthritis more than twice as likely to report serious limits on everyday activities.
- The cross-sectional design does not establish causation, and authors call for integrated, interdisciplinary care and further research into shared risk factors and mechanisms.