Overview
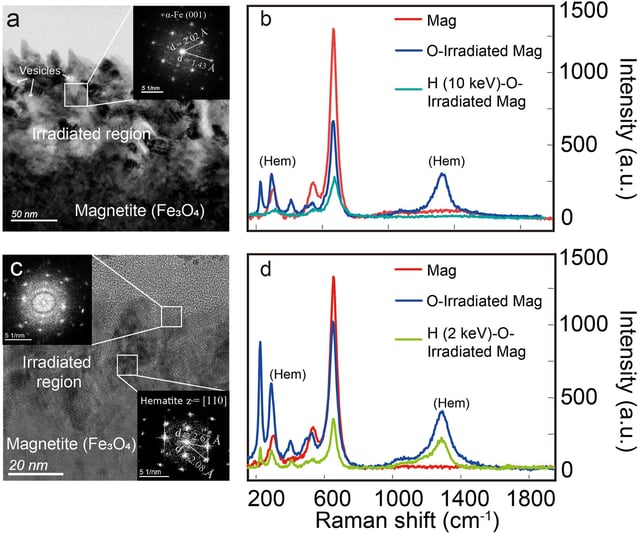
- The Macau University of Science and Technology team reports in Geophysical Research Letters that simulated Earth-origin oxygen ions produced hematite when fired at iron-bearing lunar minerals.
- Follow-up tests showed hydrogen bombardment can partially convert hematite back to iron, indicating a reversible, dynamic redox cycle on the Moon’s surface.
- Researchers focused on the monthly period of about five days when Earth shields the Moon from most solar wind, exposing it instead to charged particles escaping Earth’s atmosphere.
- The results help explain why hematite detected by Chandrayaan-1 in 2020 is concentrated at high latitudes and point to ongoing Earth–Moon material exchange.
- Scientists, including the leader of the 2020 detection, say returned samples or targeted in-situ isotope measurements are needed to confirm whether the oxygen in lunar hematite traces to Earth.