Overview
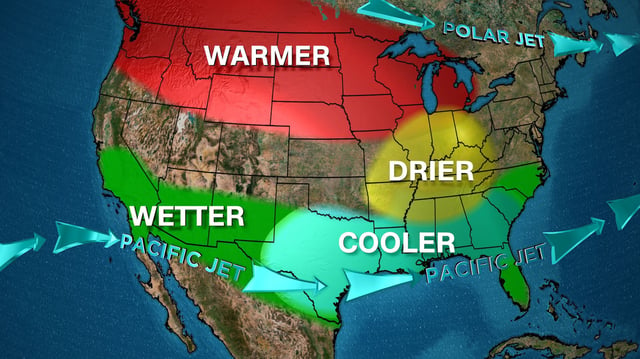
- La Niña is expected to replace the current 'super El Niño' by fall 2024, potentially impacting weather patterns globally.
- The transition to La Niña could lead to more active Atlantic hurricane seasons and drier conditions in the southern US.
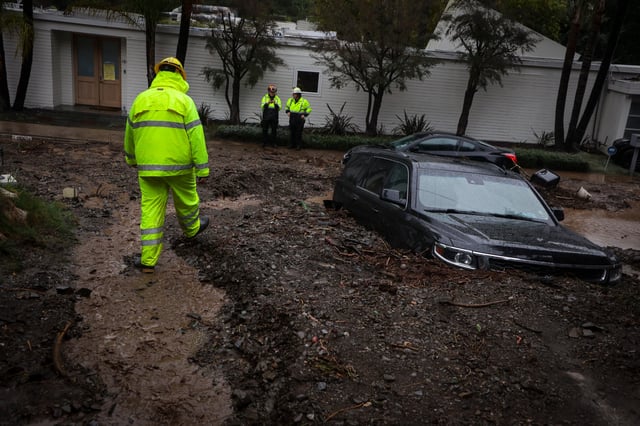
- Despite the weakening of El Niño, its effects on global weather, including warmer temperatures and storminess, may persist through April 2024.
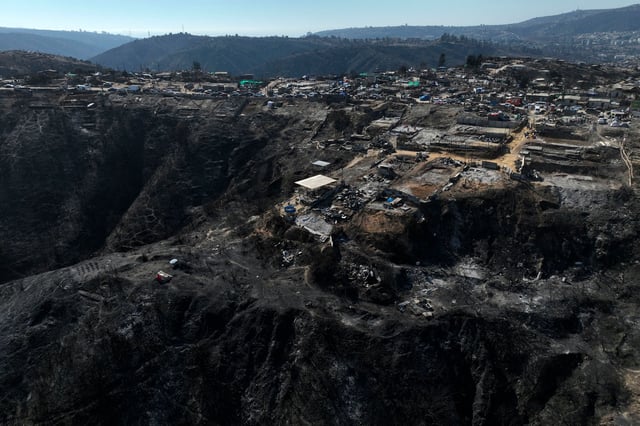
- The 'super El Niño' has contributed to record warmth globally, with January 2024 being the warmest January on record.
- Scientists are closely monitoring the transition from El Niño to La Niña, which could influence the rate of global warming and climate change.