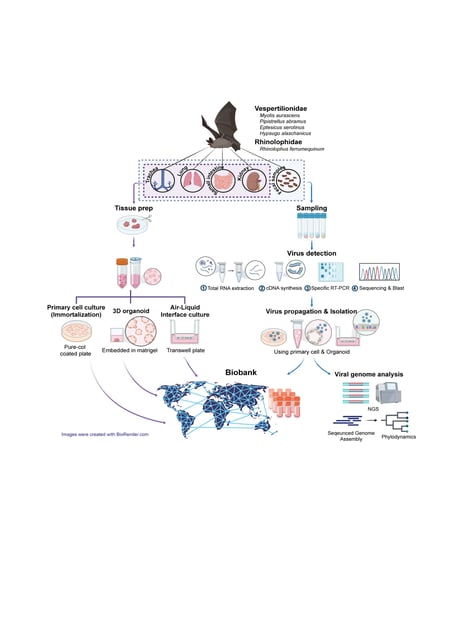
Overview
- The Institute for Basic Science (IBS) in Korea has developed a bat organoid platform using tissues from four organs across five insectivorous bat species.
- The platform revealed organ- and species-specific viral behavior for pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV, influenza A, and hantaviruses.
- Researchers discovered two new bat viruses—an orthoreovirus and a paramyxovirus—directly from wild fecal samples, one of which could not be cultured using traditional methods.
- The system allows high-throughput antiviral drug testing, with initial experiments on Remdesivir showing improved reliability over conventional lab models.
- Plans are underway to expand the platform into a global biobank, supporting international efforts to monitor, predict, and mitigate zoonotic virus outbreaks.