Overview
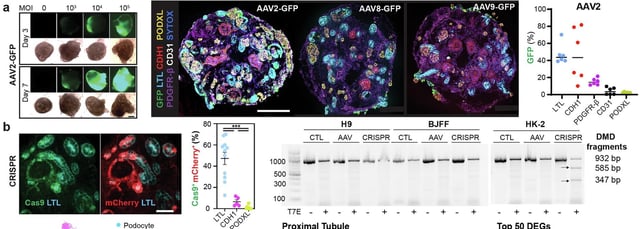
- In human kidney organoids, AAV2 activated NFκB and triggered inflammation, DNA damage, fibrosis and senescence, with proximal tubules most affected.
- These injuries occurred in the absence of gene editing, isolating the vector itself as the driver of toxicity.
- Treatment with bardoxolone methyl prevented organoid injury while preserving AAV‑mediated gene delivery.
- Authors propose integrating human organoid models into preclinical pipelines to complement animal studies and improve trial safety.
- The peer‑reviewed study appeared August 8, 2025 in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, with next steps to add vasculature, standardize protocols and seek regulatory acceptance.