Overview
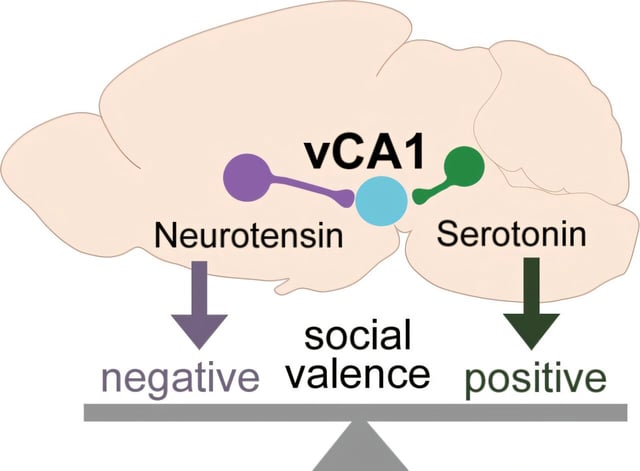
- Scientists mapped the ventral CA1 hippocampal circuitry, revealing how serotonin and neurotensin encode opposing emotional values for social interactions.
- Serotonin acting on the 1B receptor generates positive impressions, while neurotensin acting on the 1 receptor creates negative impressions of social encounters.
- A novel behavioral paradigm exposed mice to positive (potential mate) and negative (aggressive conspecific) interactions to study learned social preferences.
- Activating the serotonin 1B receptor in a mouse model of autism spectrum disorder restored positive social impressions, addressing key social deficits.
- This discovery highlights potential therapeutic targets for neuropsychiatric disorders such as autism and schizophrenia, with implications for improving social cognition.