Overview
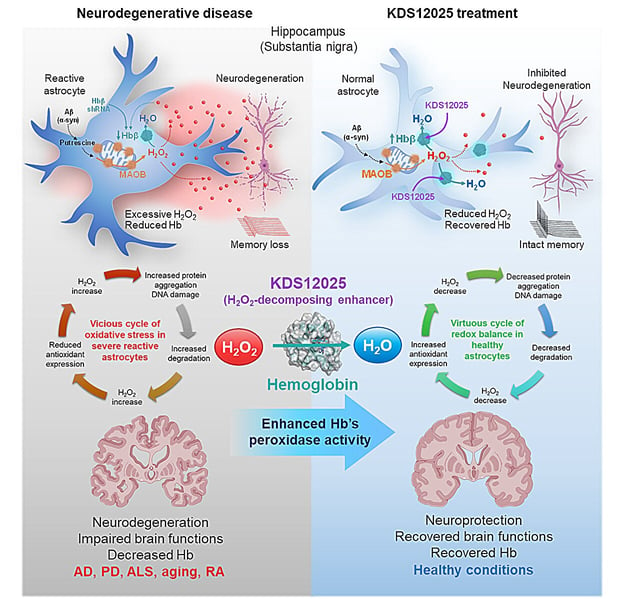
- IBS researchers report that hemoglobin resides in the nucleolus of astrocytes and acts as a pseudoperoxidase that decomposes hydrogen peroxide into water.
- KDS12025, a small water‑soluble compound, binds hemoglobin’s heme center, accelerates hydrogen peroxide breakdown by nearly 100‑fold, crosses the blood–brain barrier, and does not impair oxygen transport.
- Oral dosing in mice lowered hydrogen peroxide in diseased astrocytes, protected neurons, normalized reactive astrocytes, and restored brain function.
- In disease models, the compound delayed onset and extended lifespan in ALS mice, improved motor performance in Parkinson’s models, rescued memory in Alzheimer’s models, extended median lifespan in aging mice, and reduced inflammation and joint damage in a rheumatoid arthritis model.
- The peer‑reviewed study in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy also identified a harmful loop where excess hydrogen peroxide depletes astrocytic hemoglobin, which KDS12025 countered; the team plans isoform studies and refinement of derivatives for potential translation.