Overview
- Researchers from Japan conducted genome-wide DNA methylation mapping of the dorsal raphe nuclei in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
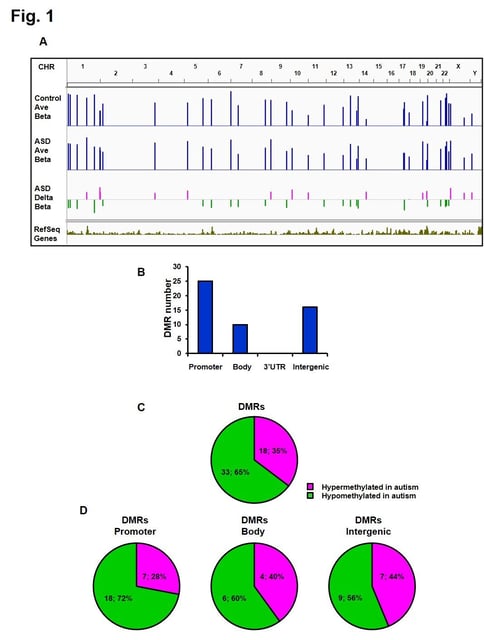
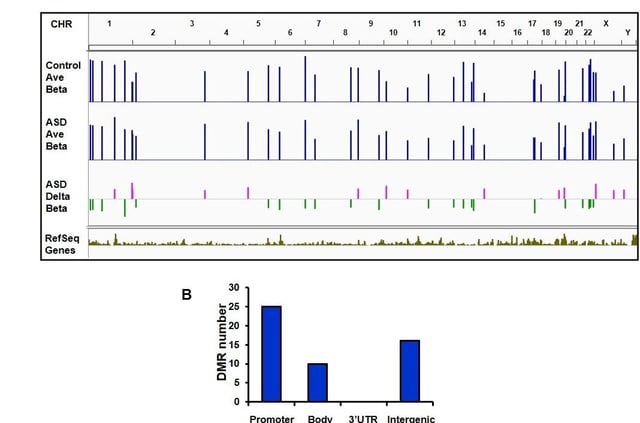
- The study identified hypermethylation in OR2C3 and HTR2C, linking these changes to sensory processing and serotonin signaling disruptions in ASD.
- A novel gene, RABGGTB, was discovered to have promoter hypomethylation and elevated expression, marking it as a new autism candidate gene absent from the SFARI database.
- The research utilized advanced methods, including the Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChip array and EM-amplicon sequencing, for detailed epigenetic analysis.
- Authors emphasize the need for integrative studies combining DNA methylation and transcriptomic data to establish causal links between epigenetic changes and gene expression.