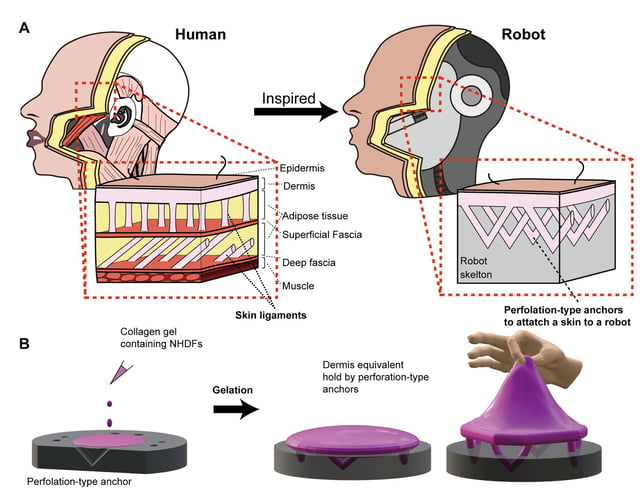
Overview
- Engineered skin mimics human ligaments, enabling flexibility and durability.
- The skin can self-repair minor cuts without external triggers.
- Potential applications include medical research, cosmetics, and plastic surgery training.
- The technique involves using collagen gel and V-shaped perforations for strong adhesion.
- Researchers aim to integrate sensory functions and humanlike expressions in future developments.