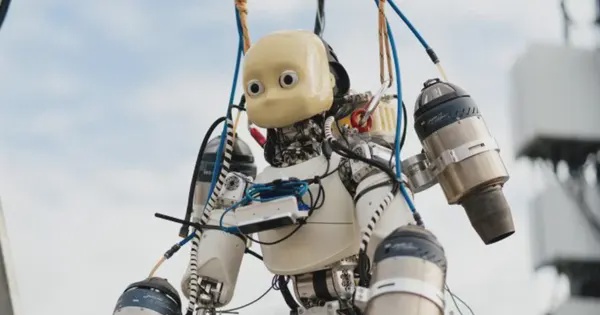
Overview
- During its initial flights, the robot lifted roughly 1.5 feet off the ground while maintaining stable hover.
- The humanoid incorporates a titanium spine and heat-resistant covers to endure jet-engine thrust forces and exhaust temperatures up to 800 °C.
- Wind tunnel experiments in August 2024 validated aerodynamic simulations and informed AI control models for real-time adjustment to turbulent airflow.
- The project brings together the Italian Institute of Technology with Stanford University’s mechanical engineering group and the Polytechnic of Milan.
- Engineers will conduct untethered flights at Genoa Airport to refine AI navigation and flight control for emergency response in extreme environments.