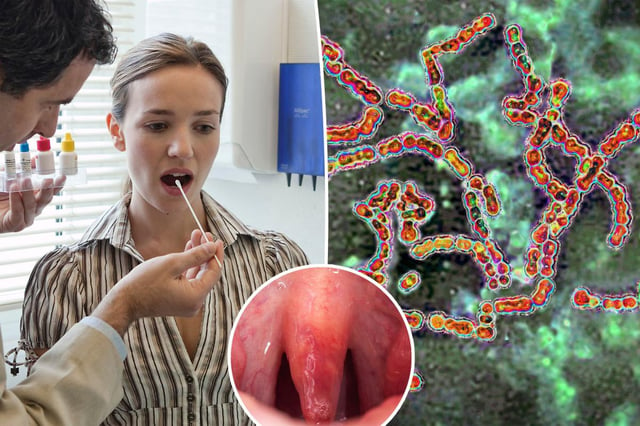
Overview
- The CDC reports invasive Group A Streptococcus (GAS) infections doubled from 3.6 to 8.2 cases per 100,000 people between 2013 and 2022.
- Over 21,000 cases and nearly 2,000 deaths were identified in a nine-year study, with severe complications like toxic shock syndrome and necrotizing fasciitis carrying a 30% mortality rate.
- High-risk groups include older adults, American Indian or Alaska Native individuals, residents of long-term care facilities, the homeless, and IV drug users.
- Factors driving the rise include increasing rates of diabetes, obesity, and intravenous drug use, particularly IV fentanyl, which facilitates infection spread.
- Emerging antibiotic-resistant strains and the rise in skin-focused infections have intensified calls for the development of a dedicated strep vaccine.