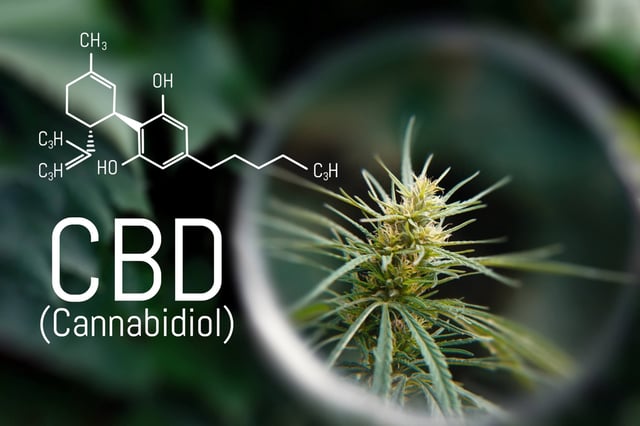
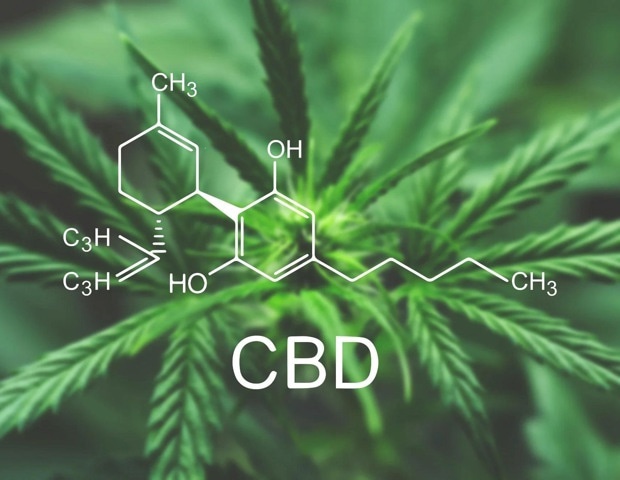
Overview
- In treated mice, expression of neuroinflammatory regulators IDO and cGAS fell, with concurrent drops in cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IFN-γ.
- Researchers administered cannabidiol by inhalation and assessed effects with flow cytometry, immunofluorescence and gene expression analyses.
- STRING-based bioinformatics highlighted AKT1, TRPV1 and GPR55 as candidate mediators of CBD’s effects, pending experimental validation.
- The authors propose CBD’s immune-calming action could complement plaque and tangle strategies, while emphasizing the findings are preclinical.
- Published Oct. 6 in the Society for Neuroscience’s eNeuro, the study was widely covered, and disclosures note a CBD inhaler licensor had no role in the research.