Overview
- The study has been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, marking a key step toward validating heavy-seed black hole formation.
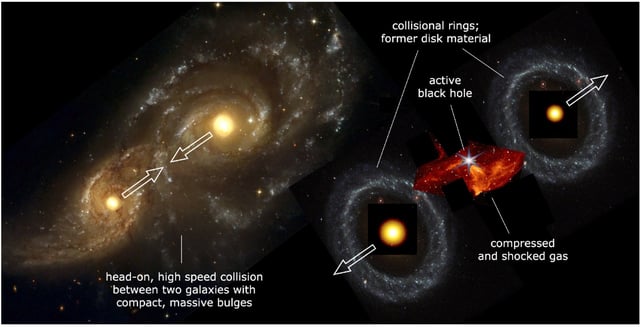
- A million-solar-mass black hole is embedded in a dense gas cloud between two merged spiral disks that together resemble the infinity symbol.
- Preliminary JWST velocity mapping shows the black hole’s motion aligns with surrounding ionized gas, consistent with an in-situ direct collapse origin.
- Follow-up Keck spectroscopy, VLA radio contours and Chandra X-ray data confirm the off-nucleus location and young age of the nascent black hole.
- Researchers are analyzing additional JWST and ancillary data to eliminate competing light-seed scenarios and seek definitive confirmation.