Overview
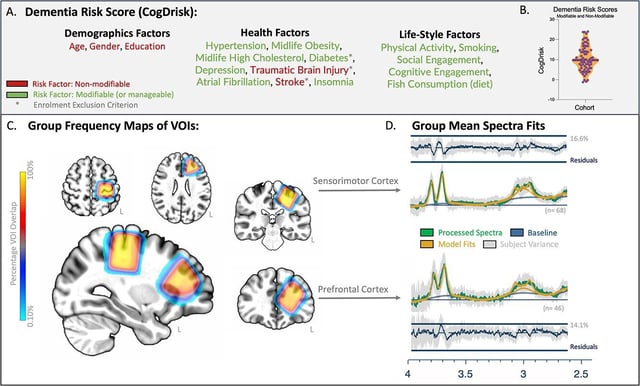
- The Thompson Institute’s study in Cerebral Cortex used magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy to quantify GABA, total N-acetylaspartate and total choline in 79 cognitively healthy older adults.
- Analysis showed that individuals with higher lifestyle-based dementia risk scores had lower GABA levels in sensorimotor regions.
- The study also found reduced concentrations of tNAA and tCho in the prefrontal cortex among participants with elevated modifiable risk profiles.
- These neurochemical shifts offer potential biomarkers for early detection of dementia years before cognitive symptoms appear.
- Researchers are now investigating how these markers can guide intervention trials focused on exercise, diet, sleep and social engagement to delay or prevent dementia.