Overview
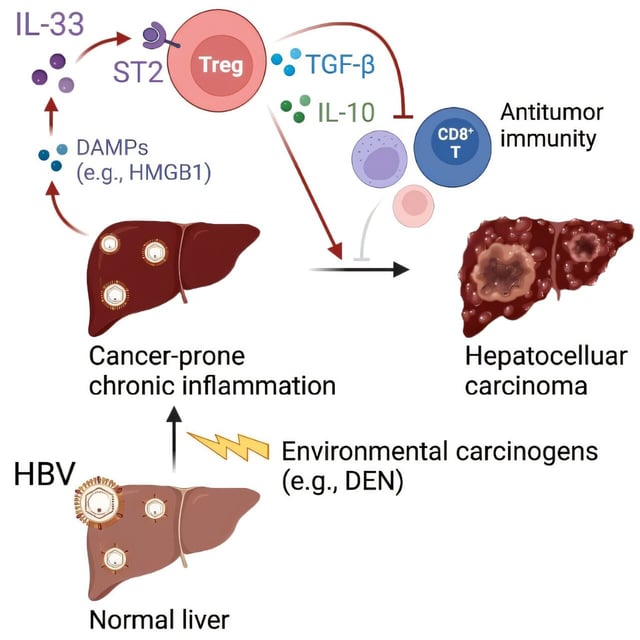
- Researchers showed that HBV infection alone does not induce liver inflammation or tumors but amplifies immune sensitivity to environmental carcinogens.
- In mouse models, exposure to the carcinogen diethylnitrosamine drove up IL-33 levels in HBV-infected livers, accelerating tumor development.
- Treatment with pitavastatin suppressed IL-33 expression in HBV-infected, carcinogen-exposed mice and cut the incidence of chronic hepatitis and cancer.
- Human samples confirmed elevated IL-33 in patients with HBV-associated chronic hepatitis compared with healthy individuals.
- Analysis of healthcare records for over 200 million HBV carriers found that statin users experienced fewer liver cancer cases and hepatitis flare-ups than those on other cholesterol-lowering drugs.