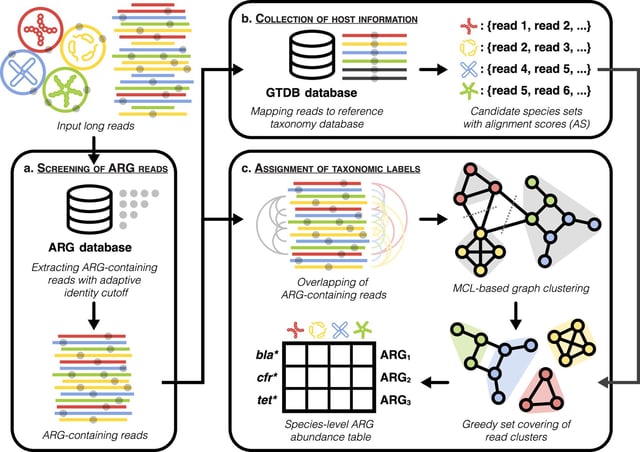
Overview
- Developed by Professor Tong Zhang's team at the University of Hong Kong, Argo addresses limitations of short-read sequencing in tracking antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs).
- The tool utilizes a read-overlapping cluster labeling approach, significantly improving host attribution and detection resolution for ARGs.
- Argo demonstrated the lowest misclassification rate in simulations and can process a 10 Gbp sample in just 20 minutes using 32 CPU threads.
- Published in Nature Communications, the study highlights Argo's potential to standardize ARG surveillance and trace dissemination pathways to combat antimicrobial resistance.
- Despite the high costs of long-read sequencing, Argo's efficiency positions it as a critical tool for advancing environmental AMR monitoring and public health efforts.