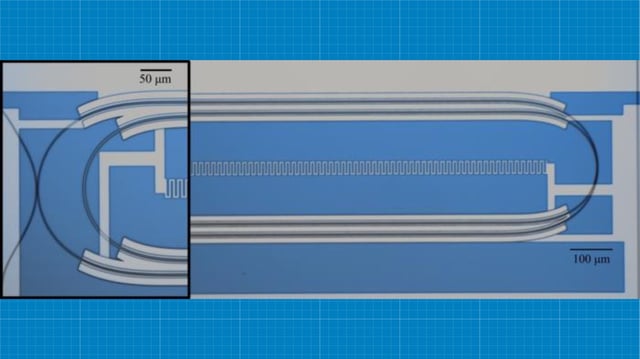
Overview
- Harvard SEAS has developed a photon router, a microwave-optical quantum transducer, that controls superconducting qubits using only light.
- The device bridges the energy gap between microwave and optical photons, allowing remote control of qubits via optical signals generated miles away.
- At just 2 millimeters in size, the router eliminates the need for bulky, heat-generating microwave cables, improving scalability and efficiency.
- This breakthrough, achieved in collaboration with Rigetti Computing, MIT, and the University of Chicago, was published in *Nature Physics* on April 2, 2025.
- Researchers are now focusing on enabling reliable entanglement generation and distribution between qubits, a critical step for quantum networks.