Overview
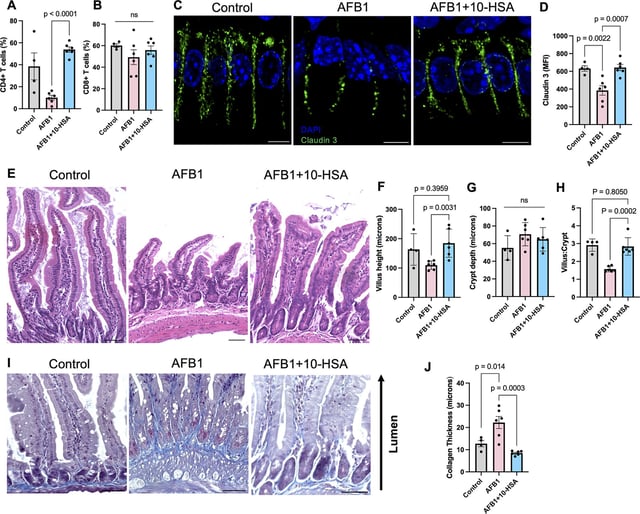
- UC Davis Health researchers published peer-reviewed results in mBio demonstrating that 10-hydroxystearic acid effectively reversed aflatoxin B1-induced liver injury and gut epithelial damage in a mouse model.
- Mechanistic studies revealed that 10-HSA acts by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, a nuclear receptor that regulates lipid metabolism and inflammation.
- Treated mice showed normalized bile acid profiles, improved hepatic energy metabolism, and restoration of gut immune responses alongside repaired epithelial barriers.
- Preclinical testing identified no cytotoxic effects of 10-HSA and indicated its activity is context-dependent on host-microbiome alignment.
- With these findings in hand, the research team is preparing to launch human clinical trials to evaluate safety and efficacy in patients with metabolic liver disorders.