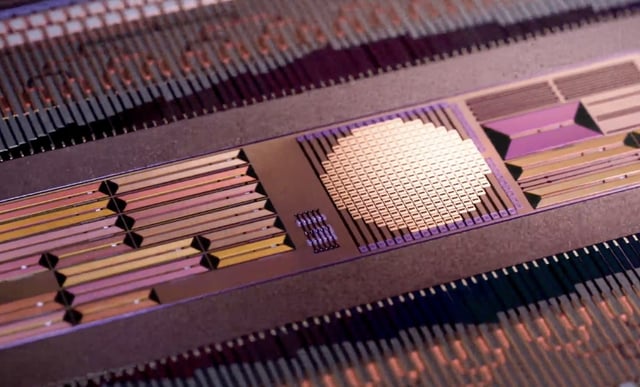
Overview
- Google's X division has unveiled a new 13mm silicon photonic chip for its Taara project, designed to transmit internet data via laser beams through the air.
- The Taara chip significantly reduces the size and complexity of previous hardware, which was as large as a traffic light, enabling faster and more cost-effective deployment.
- Taara's second-generation technology can currently transmit data at speeds of up to 10 Gbps over a 1km range, with plans to extend both range and capacity in future iterations.
- The technology has already been deployed in 12 countries, including use cases like bridging connectivity across the Congo River and supporting networks at events like Coachella.
- Experts see light-based internet as a potential solution to the growing congestion of radio frequency bands, with Taara positioned to play a key role in the future of global connectivity.