Overview
- Researchers identified glutamate dehydrogenase 1 as a novel non-steroidal therapeutic target for Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- In mdx mice, systemic R162 dosing led to significant gains in grip strength and motor coordination
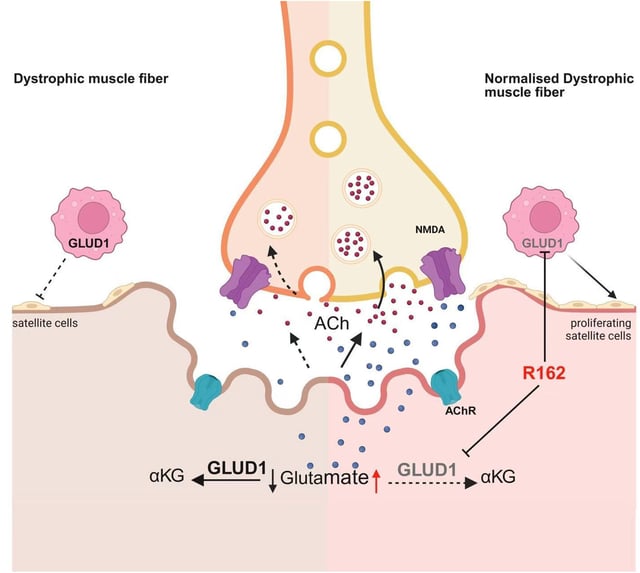
- R162 reprogrammed glutamate metabolism in dystrophic muscle, boosting satellite cell activity and restoring acetylcholine levels at neuromuscular junctions
- Macrophage-mediated regeneration proved essential for R162’s full therapeutic effect on muscle function
- Chronic R162 treatment was well tolerated with no impacts on body weight, food intake or behavior