Overview
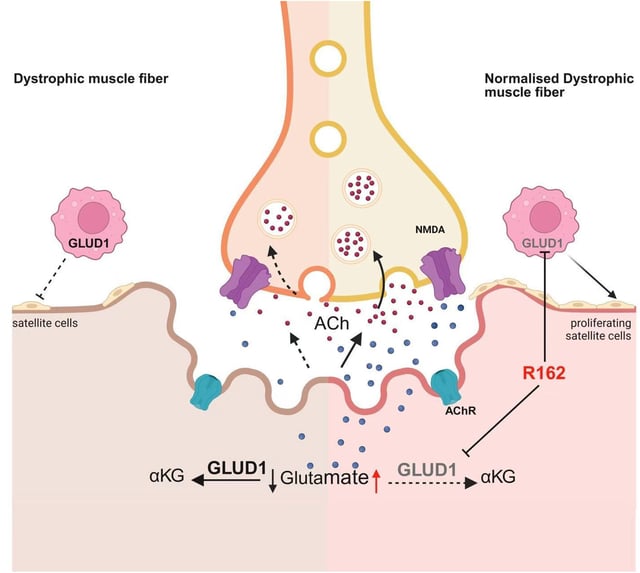
- Systemic administration of R162 significantly enhanced muscle strength, coordination and neuromuscular junction integrity in mdx mice.
- Treatment reprogrammed glutamate metabolism in dystrophic muscle, increasing local glutamate availability and restoring acetylcholine transmission.
- GLUD1 blockade reduced muscle damage and boosted the myogenic potential of satellite cells, with macrophages required for full therapeutic effect.
- R162 was well tolerated in preclinical studies, showing no adverse impacts on body weight, food intake or behavior in dystrophic mice.
- This study delivers first in-animal proof-of-concept for a non-steroidal metabolic strategy to bypass the dystrophin defect and initiates translation toward human trials.