Overview
- Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease affects about one-third of adults globally while its aggressive form, MASH, impacts roughly 5% of the population.
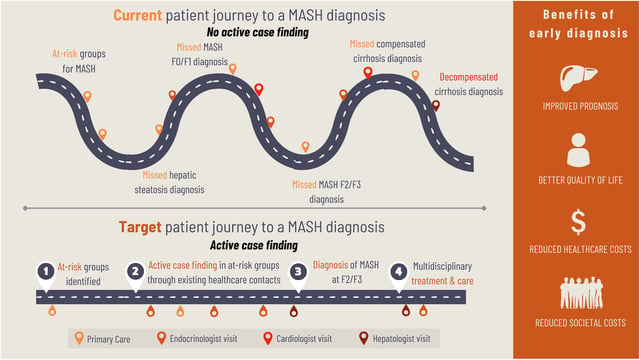
- The Global Think-tank on Steatotic Liver Disease urged health systems to double MASH diagnosis rates by 2027 through non-invasive screening and AI-driven risk stratification in primary care.
- A novel pharmacological agent has been approved for MASLD and MASH, demonstrating efficacy in halting or reversing liver inflammation and fibrosis.
- The People-First Liver Charter was published to promote person-centred language and care models aimed at reducing stigma and delaying diagnoses.
- Dr. Jeffrey Lazarus recommended that Spain’s Ministry of Health lead a national MASLD/MASH strategy featuring a disease registry, inclusion in key health indicators, automated primary care diagnostics and community-based services.