Overview
- Single-cell DLP sequencing of over 30,000 cells from 70 tumors identified WGD-high status in more than 65% of HGSOC cases.
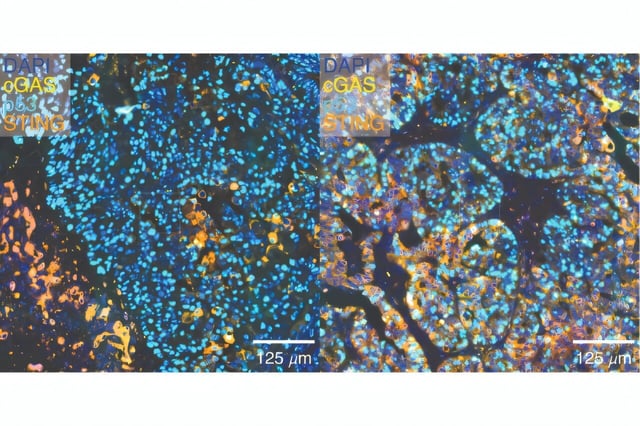
- WGD-high tumors actively repress the STING pathway, dampening innate immune activation despite high chromosomal instability.
- Evolutionary mapping placed genome doubling as a recurring event that can occur early or late and even multiple times within individual tumors.
- Increased chromosome loss and micronuclei formation after doubling underscore the link between WGD and metastasis potential.
- Next steps include development of WGD-targeted therapies and investigation of fallopian tube microenvironment triggers.