Overview
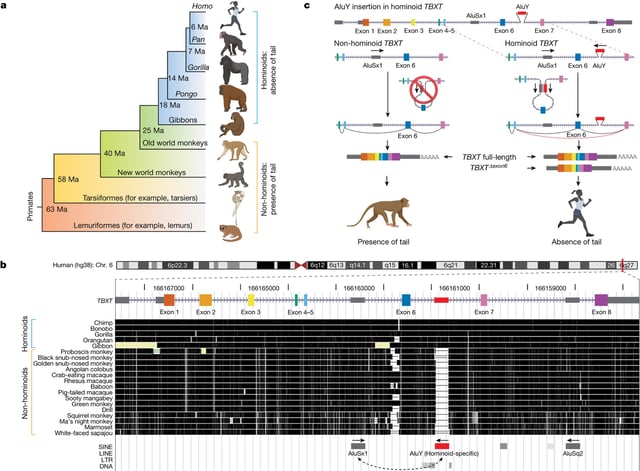
- Researchers have identified a genetic change responsible for the loss of tails in humans and other apes, pinpointing a mutation in the TBXT gene.
- The mutation involves the insertion of a DNA sequence known as an Alu element, which affects the gene's activity and protein production.
- This genetic alteration is linked to the evolutionary transition to bipedalism, facilitating upright walking and freeing hands for tool use.
- The discovery sheds light on a significant anatomical change in primate evolution, occurring approximately 25 million years ago.
- However, the mutation also increases the likelihood of developmental defects, such as spina bifida, suggesting evolutionary trade-offs.