Overview
- University of Surrey–led research reports that forskolin curbed growth of KMT2A‑rearranged acute myeloid leukemia cells in laboratory models.
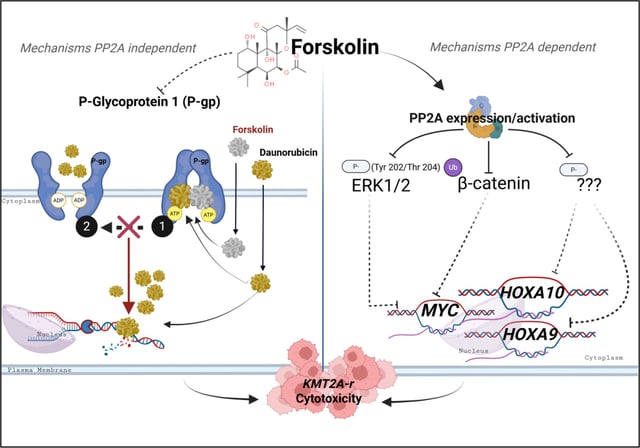
- The compound activated the tumor-suppressing enzyme PP2A and reduced expression of oncogenic drivers including MYC, HOXA9 and HOXA10.
- Forskolin also increased sensitivity to the chemotherapy drug daunorubicin by blocking P‑glycoprotein 1, a drug-efflux pump, in a PP2A‑independent effect.
- Researchers say the findings support exploring combination strategies that could allow lower chemotherapy doses and lessen toxicity, pending further validation.
- The Leukemia UK–funded work, authored by Yoana Arroyo‑Berdugo et al., appears in the British Journal of Pharmacology (DOI: 10.1111/bph.70158) and involved UK and European collaborators.