Overview
- Peer-reviewed results published August 27 in Science Advances report broad antiviral activity in cells and a strong survival benefit in a SARS-CoV-2 mouse model.
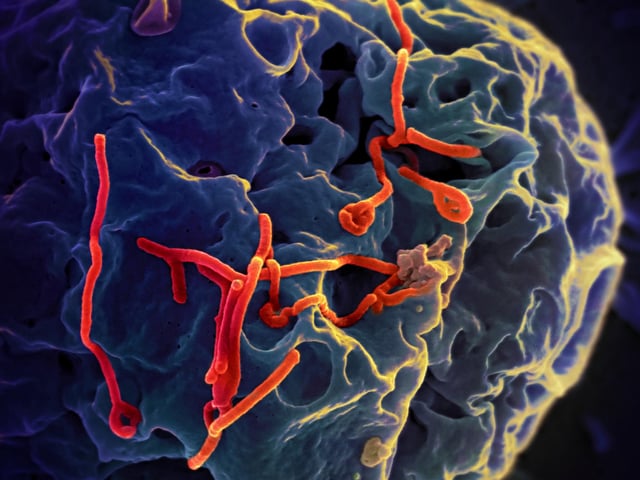
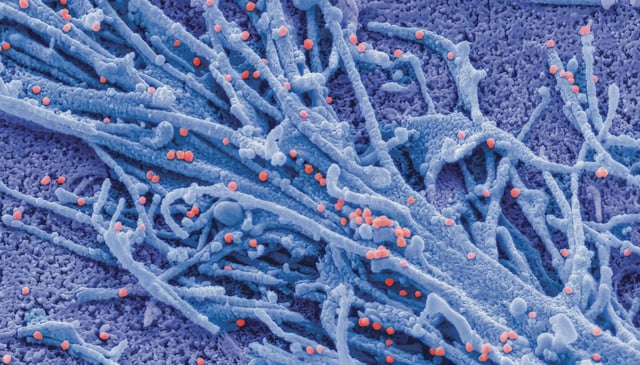
- A screen of 57 synthetic carbohydrate receptors yielded four leads that blocked infection from six viruses across three unrelated families, including Ebola, Marburg, Nipah, Hendra, SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2.
- In infected mice, a single treatment rescued about 90 percent of SARS-CoV-2 cases compared with no survivors in untreated controls.
- The lead candidate, SCR007, directly bound branched, fucosylated N-glycans on viral envelopes, and early mouse testing reported no acute toxicity at high doses.
- Researchers plan to complete preclinical development and target Phase I trials in 2028, while independent experts caution that potency, resistance, and potential effects on immune-cell glycans must be resolved.