Overview
- Researchers identified a mutational signature in gliomas associated with exposure to haloalkanes, chemicals found in fire extinguishers and flame retardants.
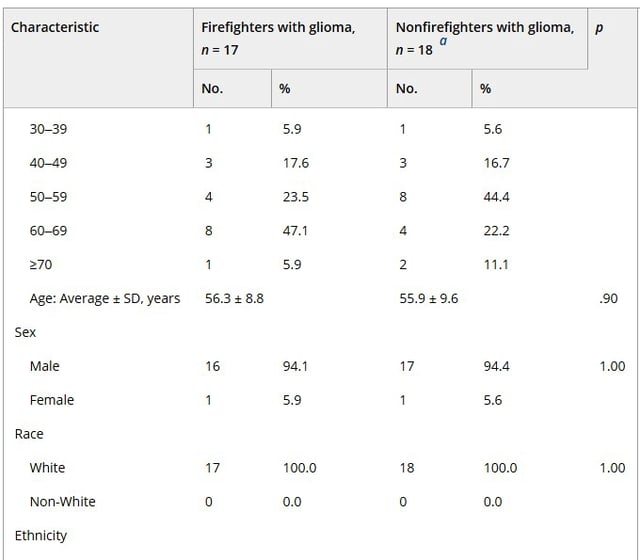
- The study analyzed tumor samples from 17 firefighters and 18 non-firefighters, revealing higher mutation rates in firefighters' tumors.
- Non-firefighters with occupational exposure to haloalkanes, such as painters and mechanics, also showed similar mutational patterns.
- The findings suggest a possible environmental risk factor for gliomas, though the study's small sample size calls for further research.
- Experts emphasize the importance of identifying occupational hazards to inform public health strategies and preventive measures.