Overview
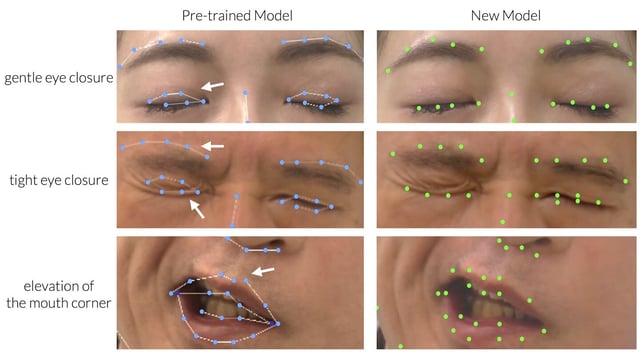
- The original 3D-FAN model failed to capture key signs of facial palsy such as eyelid closure and smile asymmetry when applied to clinical videos.
- Researchers at Kyorin University manually annotated 1,181 images from 196 patient videos to fine-tune the AI’s landmark detection through iterative machine-learning cycles.
- Post-training results showed significant error reductions in detecting facial keypoints across regions including the eyelids and mouth.
- A multidisciplinary analysis of the AI’s clinical effectiveness is underway before the team makes the model freely available to researchers and clinicians.
- The manual correction and fine-tuning method could serve as a template for developing AI-driven tools to assess other rare disorders objectively.