Overview
- Hiroshima University scientists fermented stevia leaf extract with Lactobacillus plantarum SN13T to enhance its anticancer potential
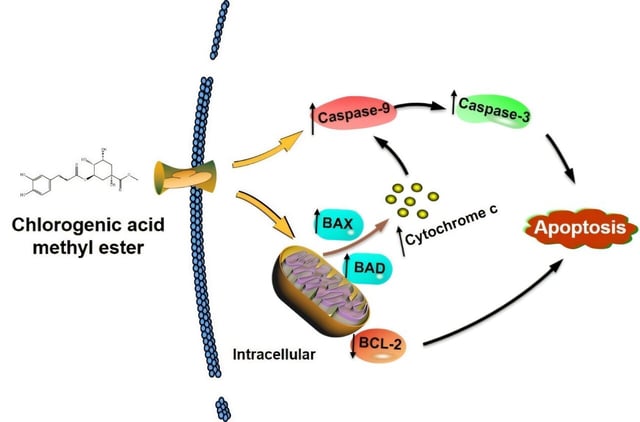
- Chemical analysis pinpointed chlorogenic acid methyl ester as the key metabolite driving apoptosis in PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cells
- In vitro tests showed that the fermented extract killed pancreatic cancer cells more effectively than non-fermented stevia at equivalent concentrations
- Human embryonic kidney cells remained largely unharmed by the fermented extract, indicating selective toxicity toward cancer cells
- The team will advance to mouse model experiments to assess systemic efficacy and determine optimal dosing in vivo