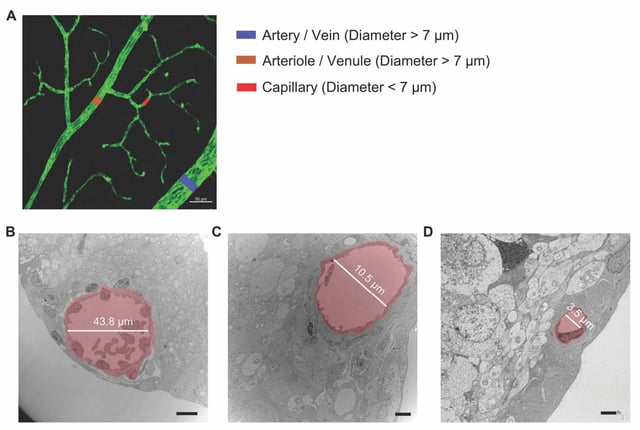
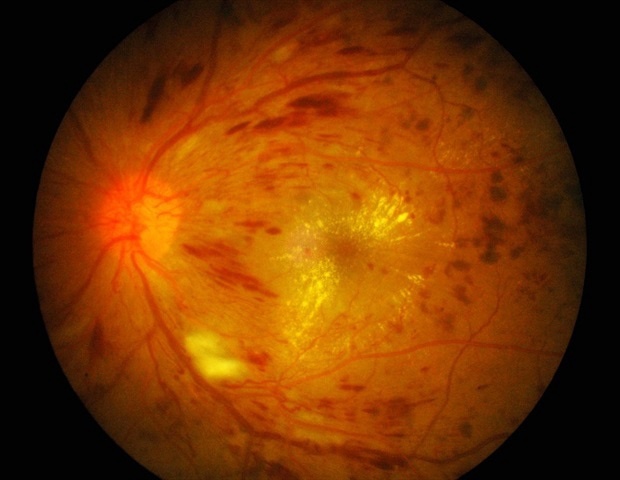
Overview
- A Johns Hopkins-led study reveals that hypoglycemia in diabetic mice triggers HIF protein accumulation, leading to blood-retinal barrier breakdown and vascular leakage.
- The blood-retinal barrier disruption contributes to irreversible retinal damage and vision loss in diabetic retinopathy, a major complication of diabetes.
- Researchers tested the experimental drug 32-134D, which inhibits HIF and successfully prevented retinal damage in diabetic mice during hypoglycemia.
- The findings, published in *Science Translational Medicine* on April 30, 2025, offer a potential pathway for new therapies targeting diabetic vision loss.
- Plans are underway to conduct clinical trials of 32-134D to evaluate its safety and efficacy in human patients with diabetic retinopathy.