Overview
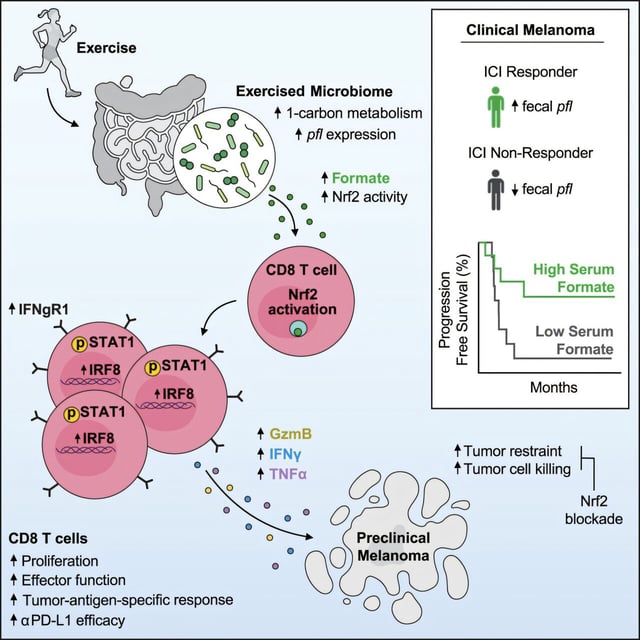
- In melanoma-bearing mice, a four-week exercise regimen shrank tumors and extended survival but lost its effect when gut microbes were removed
- Machine learning analysis pinpointed formate as the key exercise-induced microbial metabolite driving anti-tumor CD8 T-cell activity
- Daily oral formate in mouse models of melanoma, adenocarcinoma and lymphoma markedly inhibited tumor growth and strengthened responses to checkpoint inhibitors
- In advanced melanoma patients undergoing immunotherapy, higher blood formate levels correlated with longer progression-free survival
- Fecal transplants from high-formate donors enhanced T-cell activation and tumor control in mice, and researchers are now assessing formate as an adjuvant therapy