Overview
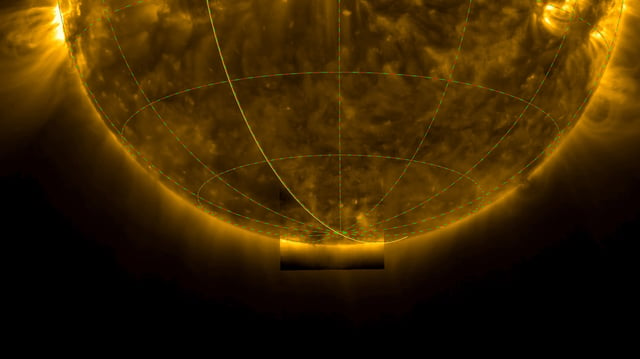
- The Solar Orbiter spacecraft achieved a 17-degree tilt above the ecliptic to capture the first-ever views of the Sun’s south pole.
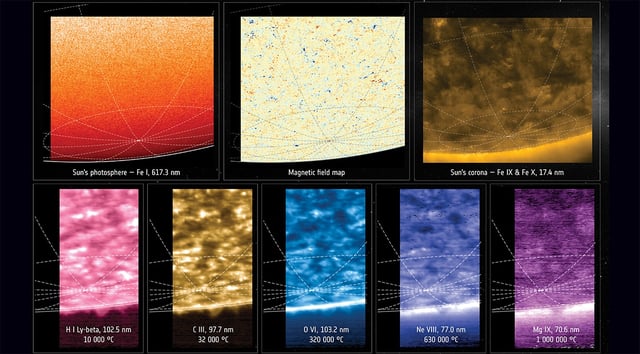
- PHI measurements reveal mixed north and south polarities tangled in a chaotic field at the Sun’s south pole.
- The SPICE spectrograph mapped plasma velocities near the pole, revealing insights into the origins of the solar wind.
- These real-time observations document the polar magnetic inversion at the height of the Sun’s 11-year activity cycle.
- The probe will raise its inclination to 24 degrees by late 2026 and to 33 degrees by mid-2029 for continued polar monitoring.