Overview
- ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), a rare and aggressive T-cell lymphoma primarily affecting children and young adults, often develops resistance to existing treatments.
- The HDAC inhibitor entinostat demonstrated the ability to significantly delay or prevent lymphoma onset in preclinical models and showed efficacy in therapy-resistant patient cells.
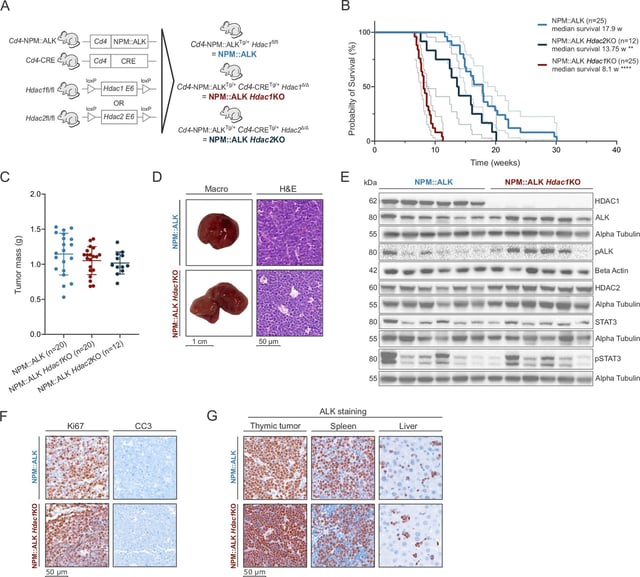
- Unexpectedly, genetic silencing of the enzyme HDAC1 accelerated tumor growth, revealing its protective role in certain stages of lymphoma progression.
- Loss of HDAC1 was found to alter chromatin structure and activate oncogenic signaling pathways, including PDGFRB-STAT5 and T cell receptor-associated mechanisms, driving tumor proliferation.
- The findings emphasize the need for precision in HDAC-targeted therapies and support advancing entinostat into clinical trials for resistant ALK-positive ALCL cases.