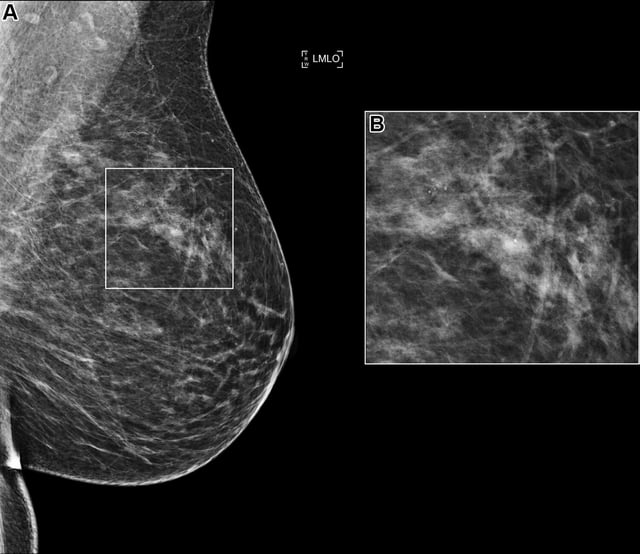
Overview
- The algorithms demonstrated a median specificity of 98.7% and a sensitivity of 27.6% with a 1.7% recall rate on independent mammography exams.
- Combining the top three models raised sensitivity to 60.7% and the top ten ensemble reached 67.8%, narrowing the gap with average screening radiologists.
- Individual model performance varied by cancer subtype, imaging equipment manufacturer and clinical site, with stronger detection of invasive cancers than noninvasive lesions.
- Many leading submissions are open source and rely on publicly available training data, creating a shared resource for standardized benchmarking and iterative improvement of mammography AI.
- Researchers plan follow-up studies to compare top Challenge models against commercial tools using larger, more diverse datasets and human reader test sets such as the PERFORMS scheme.