Overview
- A study published in PNAS on August 5 shows RcoM-HBD-CCC cuts carbon monoxide half-clearance time in mouse blood to under a minute compared with over an hour using oxygen therapy.
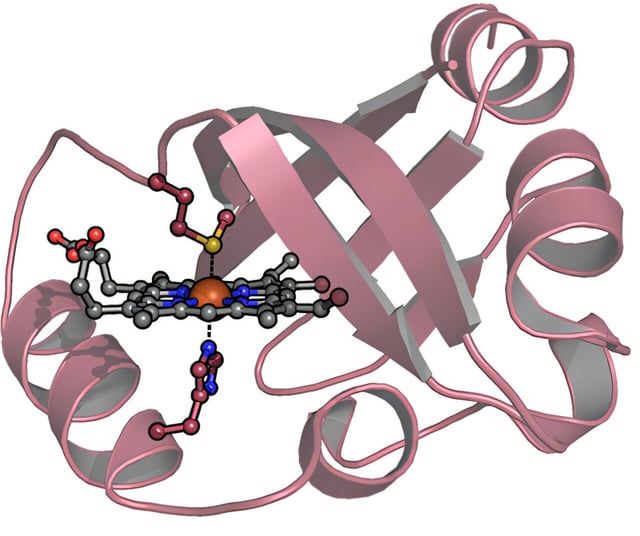
- RcoM-HBD-CCC produced minimal blood pressure changes in mice, overcoming a key limitation of prior hemoprotein-based CO scavengers that often cause vasoconstriction.
- The therapy is built on an engineered RcoM scaffold derived from Paraburkholderia xenovorans, achieving high selectivity for CO without binding oxygen or other vital molecules.
- Researchers disclosed a provisional patent filed at the University of Pittsburgh and licensed the technology to Globin Solutions, signaling a clear commercialization pathway.
- Next steps include additional dose-ranging and safety assessments in preclinical models and discussions with regulators before moving into human trials.