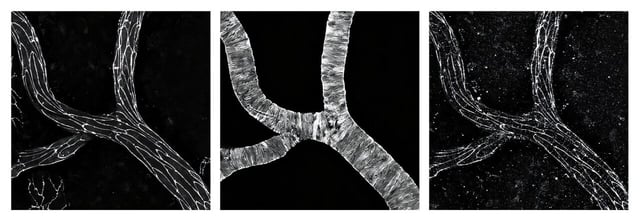
Overview
- Harvard researchers showed that endothelial cells lining cerebral arteries form gap junction networks to transmit vasodilation signals within seconds of neural activation.
- The Cell paper pinpoints connexin proteins Cx37 and Cx40 as critical molecular components for arterial gap junction coupling.
- Targeted deletion of Cx37 and Cx40 in mouse endothelial cells abolished long-range vasodilation and impaired dynamic blood flow regulation.
- Given the conservation of mammalian brain vasculature, the team expects these findings to improve functional MRI accuracy by linking imaging signals directly to cellular mechanisms.
- Future work will test this signaling pathway in human tissues and explore its potential as a therapeutic target for neurodegenerative disorders.