Overview
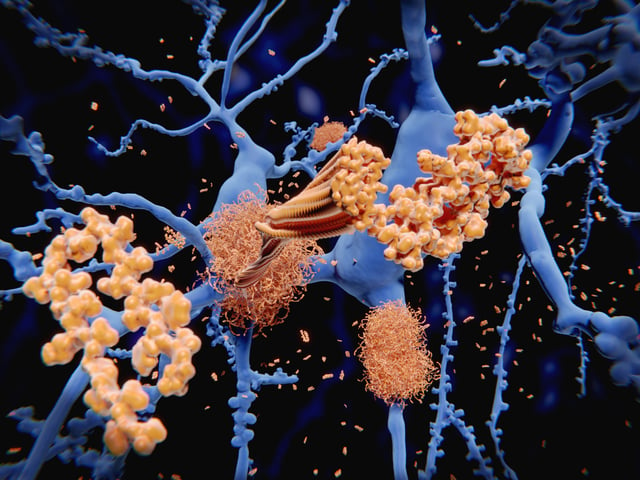
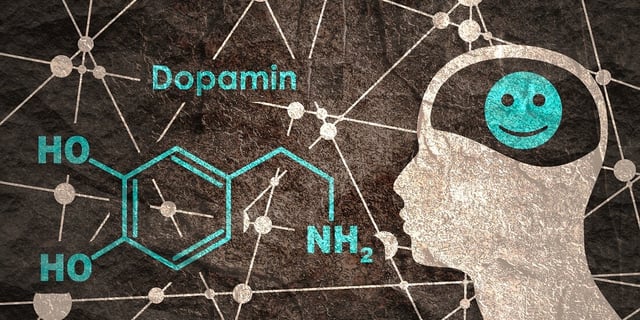
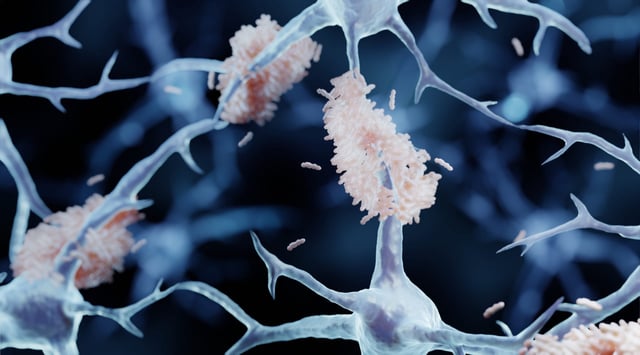
- Dopamine boosts neprilysin, an enzyme that degrades beta-amyloid plaques linked to Alzheimer's.
- L-DOPA treatment in mice led to reduced plaques and improved memory function.
- Neprilysin levels naturally decrease with age, potentially serving as an early Alzheimer's biomarker.
- Further research needed to understand dopamine's regulation of neprilysin and manage L-DOPA's side effects.
- Human trials are required to confirm the effectiveness of dopamine-based treatments for Alzheimer's.